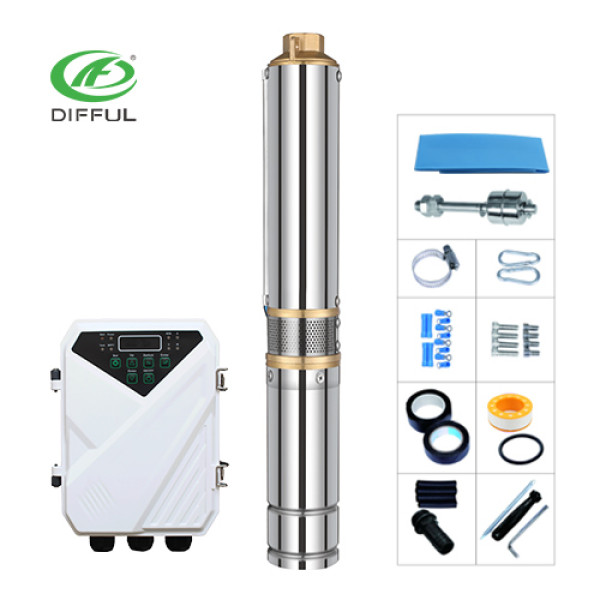
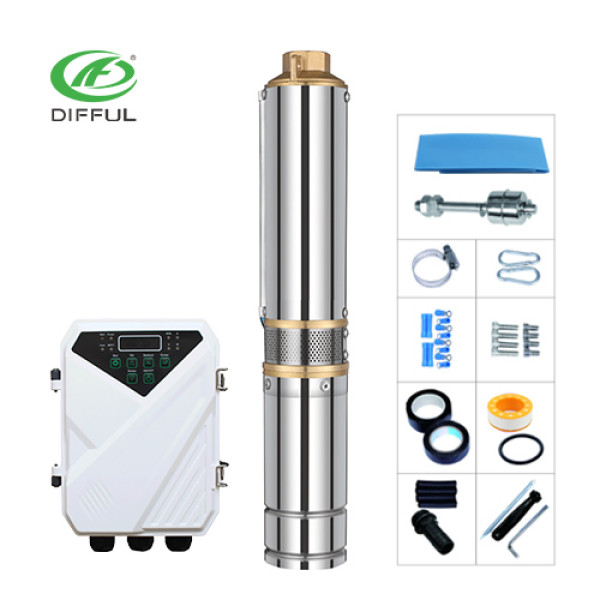
Search This Supplers Products:PUMPAC/DC SOLAR PUMPDC SOLAR PUMPSURFACE PUMPSUBMERSIBLE PUMPPOOL PUMP
Market Demand Analysis of Wholesale Solar Submersible Pumps: The Shift Toward Energy-Efficiency and Sustainability
time2024/11/29
- The global market for solar submersible pumps is growing rapidly, driven by the demand for energy-efficient, sustainable water solutions. Advancements in solar technology, along with government incentives and environmental concerns, are fueling adoption. These pumps offer cost-effective alternatives for irrigation and water supply, particularly in off-grid areas. This article explores market trends, key drivers, and future prospects for solar-powered water pumping systems.
The global demand for solar-powered submersible pumps has been steadily rising, driven by a convergence of factors including the need for energy-efficient solutions, advancements in solar technology, and growing environmental consciousness. As industries and households seek alternatives to traditional, grid-dependent pumping systems, the wholesale market for solar submersible pumps is experiencing significant growth. This article explores the changing demand for solar submersible pumps, particularly focusing on the growing demand for energy-efficient models in the wholesale market.
1. Overview of Solar Submersible Pumps
Solar submersible pumps are a type of pump designed to be powered by solar energy. These pumps are typically submerged in a water source, such as a well or borehole, and are used for applications like irrigation, drinking water supply, drainage, and industrial processes. The solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which powers the pump, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to conventional electric or diesel-powered pumps.
Unlike traditional pumps that rely on the electricity grid or fuel, solar submersible pumps offer the advantage of operating in remote and off-grid locations, where electrical infrastructure may be lacking or unreliable. They are also increasingly used in both urban and rural areas due to their cost-effectiveness and sustainability.
2. Global Market Demand Trends
The global market for solar submersible pumps has seen rapid growth in recent years. This demand surge can be attributed to several interrelated factors, particularly energy efficiency, environmental concerns, and the broader shift toward renewable energy sources.
A. Energy Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness
Energy efficiency is one of the foremost driving forces behind the increased demand for solar submersible pumps. Conventional pumping systems, especially those that rely on diesel or grid electricity, are becoming less viable due to rising fuel costs and electricity prices. In contrast, solar pumps are increasingly seen as a long-term, cost-effective solution due to the falling prices of solar panels and advances in pump technology.
Solar-powered pumps have low operational costs. Once the initial investment is made, they require minimal maintenance and no fuel or electricity charges. In regions with abundant sunlight, the return on investment for solar submersible pumps is attractive, with many systems paying for themselves in 3 to 5 years.
B. Environmental Concerns and Sustainability
The growing concern about climate change and the environmental impact of fossil fuel-based energy sources has led to a global push for more sustainable solutions. Solar submersible pumps, which rely on clean, renewable energy, align well with this push. Governments, NGOs, and corporations worldwide are increasingly prioritizing renewable energy technologies, and solar-powered pumps are viewed as a key part of this shift.
For rural and developing areas, solar submersible pumps can provide reliable access to water for irrigation and drinking without contributing to environmental degradation. This aspect is especially important in regions suffering from water scarcity and frequent power outages, where solar-powered pumps offer a more resilient and sustainable alternative.
C. Technological Advancements in Solar Pumps
As solar technology continues to advance, solar submersible pumps have become more efficient, durable, and affordable. In recent years, pump manufacturers have focused on improving the efficiency of solar panels, optimizing pump motors, and integrating smart technologies such as sensors and remote monitoring. These technological improvements are driving down costs and increasing the reliability and effectiveness of solar-powered pumping systems.
The integration of IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) in pump systems also allows for better monitoring, predictive maintenance, and energy optimization, further boosting the attractiveness of solar submersible pumps in both residential and industrial applications.
D. Government Incentives and Policy Support
Governments across the globe are offering subsidies, incentives, and favorable policies to encourage the adoption of renewable energy technologies. In many countries, including India, the United States, and parts of Africa, governments have rolled out financial incentives for the installation of solar-powered pumps, especially for agricultural use.
These incentives, which can include tax breaks, low-interest loans, and grants, are helping reduce the initial cost of solar submersible pumps, making them more accessible to farmers and businesses in rural and off-grid areas.
3. Regional Demand Dynamics
The demand for solar submersible pumps varies across regions, with particular growth observed in areas with large agricultural sectors and limited access to electricity.
A. Asia-Pacific
The Asia-Pacific region is witnessing the most significant growth in solar submersible pump demand, primarily driven by countries like India, China, and parts of Southeast Asia. In India, for example, solar submersible pumps are being promoted under the government's “Pradhan Mantri Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan (PM KUSUM)” scheme, which aims to provide solar pumps to farmers for irrigation. Similarly, China, as a major producer and consumer of solar technology, is also seeing a rapid adoption of solar pumps for both agricultural and industrial applications.
B. Africa
In Africa, where many regions still rely on diesel or manual pumps for water supply, the transition to solar-powered pumps is gaining traction. Sub-Saharan Africa, in particular, is expected to see robust growth in solar pump installations due to the high solar insolation levels and the need for reliable water supply in rural and peri-urban areas. International organizations and NGOs are also investing heavily in solar-powered water projects to improve access to clean water.
C. Latin America and the Middle East
Latin America, with its strong agricultural base, is seeing an increase in demand for solar pumps for irrigation. Countries such as Brazil, Argentina, and Mexico are particularly active in adopting solar technology to address water scarcity issues. Meanwhile, the Middle East, which suffers from extreme water shortages, is increasingly turning to solar-powered solutions as part of broader sustainability initiatives.
4. Key Drivers and Challenges
Key Drivers
a.Cost Savings: Long-term savings on electricity or fuel costs drive demand.
b.Energy Independence: Off-grid areas rely on solar pumps for autonomous water access.
c.Sustainability: The growing preference for green and sustainable technologies is a major factor.
d.Rising Energy Prices: Traditional energy sources like diesel are becoming costlier, making solar pumps more attractive.
e.Government Policies: Subsidies and incentives are accelerating adoption, particularly in agricultural sectors.
Challenges
a.High Initial Costs: While operational costs are low, the upfront investment for solar systems can still be a barrier for some consumers, especially in low-income regions.
b.Lack of Technical Knowledge: In some areas, the technical expertise to install and maintain solar systems can be limited.
c.Intermittent Energy Supply: Solar-powered systems are dependent on sunlight, which can be intermittent in regions with inconsistent weather patterns.
5. The Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the demand for solar submersible pumps is expected to continue its upward trajectory as the world increasingly embraces renewable energy solutions. Technological advancements will further reduce costs, increase efficiency, and broaden the applicability of solar pumps. With supportive policies and growing environmental awareness, solar-powered submersible pumps are set to play an essential role in addressing global water and energy challenges.
Wholesale suppliers of solar submersible pumps will likely focus on enhancing product performance, expanding into new markets, and responding to the growing demand for energy-efficient solutions. The future of the solar pump industry lies in its ability to combine sustainability with cost-effectiveness, meeting the needs of a diverse range of consumers, from farmers in remote regions to industries in urban centers.
Conclusion
The wholesale market for solar submersible pumps is undergoing a transformative shift driven by technological advances, the need for energy-efficient solutions, and growing environmental concerns. As demand for these pumps continues to rise across various regions, manufacturers, distributors, and governments must collaborate to expand access, improve affordability, and ensure sustainability. With the right investments in innovation and infrastructure, solar submersible pumps are poised to become a key component of the global shift toward renewable energy and resource conservation.
DIFFUL is an innovative and technology-leading manufacturer of solar pumps, specializing in DC solar pumps, AC/DC hybrid solar pumps, and shielded motor solar pumps. Since our establishment in 1989, we have maintained a 100% focus on this industry, with hundreds of thousands of our pumps in use worldwide. Our commitment to quality is evident through the use of high-precision and fully automatic processing machines, advanced assembly lines, and testing equipment to enhance efficiency and ensure top-notch products. Furthermore, we have established our own controller production and research and development workshop, guaranteeing that every step of the production process is meticulously controlled. We are actively seeking Distributors and offer support for OEM partnerships. If there are any further discussions or details that need to be addressed, please feel free to contact us. We appreciate your attention and trust.
E-mail:sales08..........com
Tel/WhatsApp:+86 15058288607
DIFFUL solar power surface centrifugal pumps surface water solar pump surface water irrigation pump solar surface pump india
4-inch AC/DC Hybrid pump with Plastic impeller solar pump for agriculture purpose, Factory direct sales.
solar powered pump for domestic water supplying and irrigation in Australia
dc solar pump manufacturers in china
4inch DC brushless solar submersible pump price Plastic impeller solar powered pump for agriculture purpose in South Africa




